
Suitable for
Development age between ≈ 2 and 10 years
Questionnaire type
Image questionnaire
Duration
10 to 15 min
Construct
Interest in technology as a personality trait of children in pre and primary school.
Level of development
Development level
Number of items
25
Scale level
Likert scale
Instruction
‚Please choose which one you like best.‘
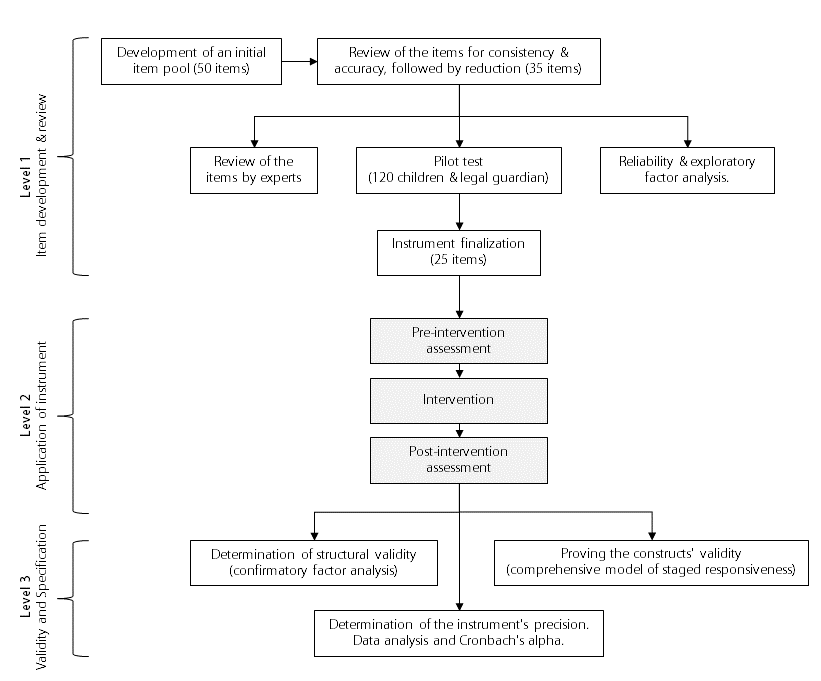
Content
The Children’s Technology Interest Questionnaire (CTI) is a picture survey with 25 questions aimed at children in the pre-school and primary school years. The instrument measures the level of interest displayed by children towards technology at a developmental age range of approximately 2 to 10 years. The picture questionnaire takes 10 to 15 minutes to complete and is based on the nominal and Likert scale. The children are told to pick the picture they like the most out of the two shown: ‚Please choose which one you like best.‘ The process of constructing and evaluating the CTI is premised on the notion that a fascination with technological advancements is a personal disposition that can be attributed to psychological factors. A personal interest in technology is a person’s inner bias or conviction in relation to technical topics or objects.
